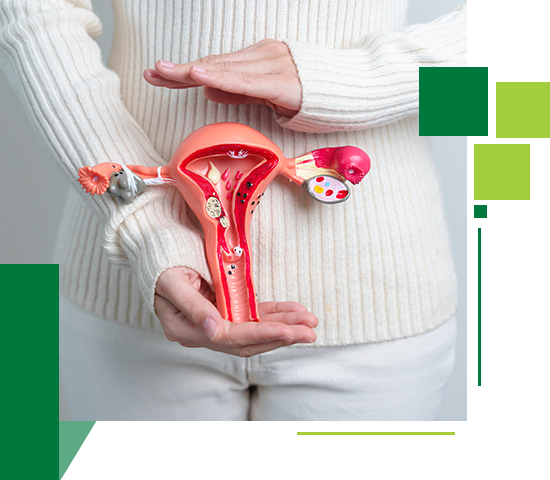
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) are two conditions that are often used interchangeably, there’s a difference between the two. PCOD is an imbalance of hormones that results in enlarged follicles in the ovaries. Typically, the ovaries only release a small quantity of male hormones known as androgens throughout the menstrual cycle. But in PCOD cases, the ovaries will start producing androgens in excess which can cause weight gain, irregular menstrual cycles, and infertility.
Alternatively, PCOS is a hormonal condition that can result in the development of numerous cysts within the ovaries. In this, the ovaries produce higher levels of androgen than usual, which interferes with the development and release of the eggs. It has a lot of symptoms common with PCOD such as irregular periods, excess body hair, acne, infertility, and weightgain.
Having higher than normal androgen levels can affect your health which may cause complications like abnormal uterine bleeding, infertility, type 2 diabetes, preterm labor and preterm birth, metabolic syndrome, depression, and miscarriage. The physical exam, ultrasound, and blood tests can help diagnose PCOD and PCOS.

 Causes and risk factors
Causes and risk factors
PCOD/PCOS is often linked to abnormal hormone levels and other factors such as:
Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance is a common factor in the development and persistence of PCOS. Being overweight does not respond normally to insulin which can lead to higher production of testosterone hormones and a variety of other symptoms.
Hormone Imbalance: Hormonal Imbalance can produce unusually high levels of androgen which results in irregular menstrual cycles, missed periods, and unpredictable ovulation.
Inflammation: Inflammation may affect the normal function of the ovaries which can interfere with ovulation, lowering the chance of ovaries releasing the healthy egg.
 Solutions from navayur
Solutions from navayur
-
Rated 0 out of 5
-
Rated 0 out of 5